



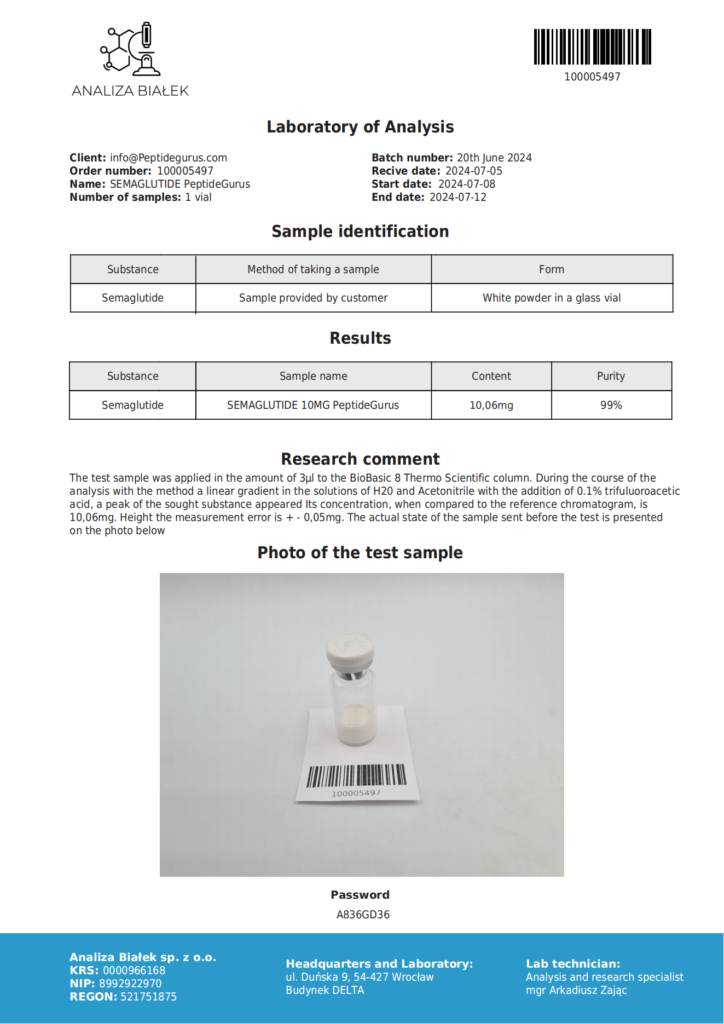

Categories: Peptide Finished product, Peptides and Their Dosages
Semaglutide is a derivative of the naturally occurring GLP-1, a peptide known to lower blood sugar levels and enhance insulin secretion. Research shows that Semaglutide may also improve heart, liver, and lung function while helping to slow or prevent the effects of Alzheimer’s disease. Semaglutide has been shown to significantly decrease appetite by delaying gastric emptying and reducing intestinal motility. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Analog Shown to Stimulate Insulin and Suppress Glucagon Secretion in a Glucose-Dependent Manner.
Free (1) 30 ml Bacteriostatic Water
with qualified orders over $500 USD.
(excludes capsule products, cosmetic peptides, promo codes and shipping)
Semaglutide is a derivative of the naturally occurring GLP-1, a peptide known to lower blood sugar levels and enhance insulin secretion. Research shows that Semaglutide may also improve heart, liver, and lung function while helping to slow or prevent the effects of Alzheimer’s disease. Semaglutide has been shown to significantly decrease appetite by delaying gastric emptying and reducing intestinal motility. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Analog Shown to Stimulate Insulin and Suppress Glucagon Secretion in a Glucose-Dependent Manner.
Product Usage: This PRODUCT IS INTENDED AS A RESEARCH CHEMICAL ONLY. This designation allows the use of research chemicals strictly for in vitro testing and laboratory experimentation only. All product information available on this website is for educational purposes only. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law. This product should only be handled by licensed, qualified professionals. This product is not a drug, food, or cosmetic and may not be misbranded, misused or mislabled as a drug, food or cosmetic.
GLP-1, short for glucagon-like peptide-1 is a short, naturally occurring peptide hormone just 30-31 amino acids in length. Its primary physiologic function is to lower blood sugar levels by naturally enhancing insulin secretion. It also plays roles in protection beta cell insulin stores by promoting insulin gene transcription and has been linked with neurotrophic effects in the brain and central nervous system. In the GI system, GLP-1 has been shown to significantly decrease appetite by delaying gastric emptying and reducing intestinal motility. Preliminary research has shown impacts of GLP-1 in the heart, fat, muscles, bones, liver, lungs, and kidneys as well.
The primary focus of GLP-1 research has been in the realm of diabetes treatment/prevention as well as appetite suppression. Secondary research focuses on the potential cardiovascular benefits of the peptide. More recent, and thus less robust, research focuses on the ability of GLP-1 to stave off neurodegenerative disease. Though this latter area of research is newest, it is also the fast-growing area of GLP-1 study now that the peptide has been revealed to slow or prevent the accumulation of amyloid beta plaques in the setting of Alzheimer’s disease.
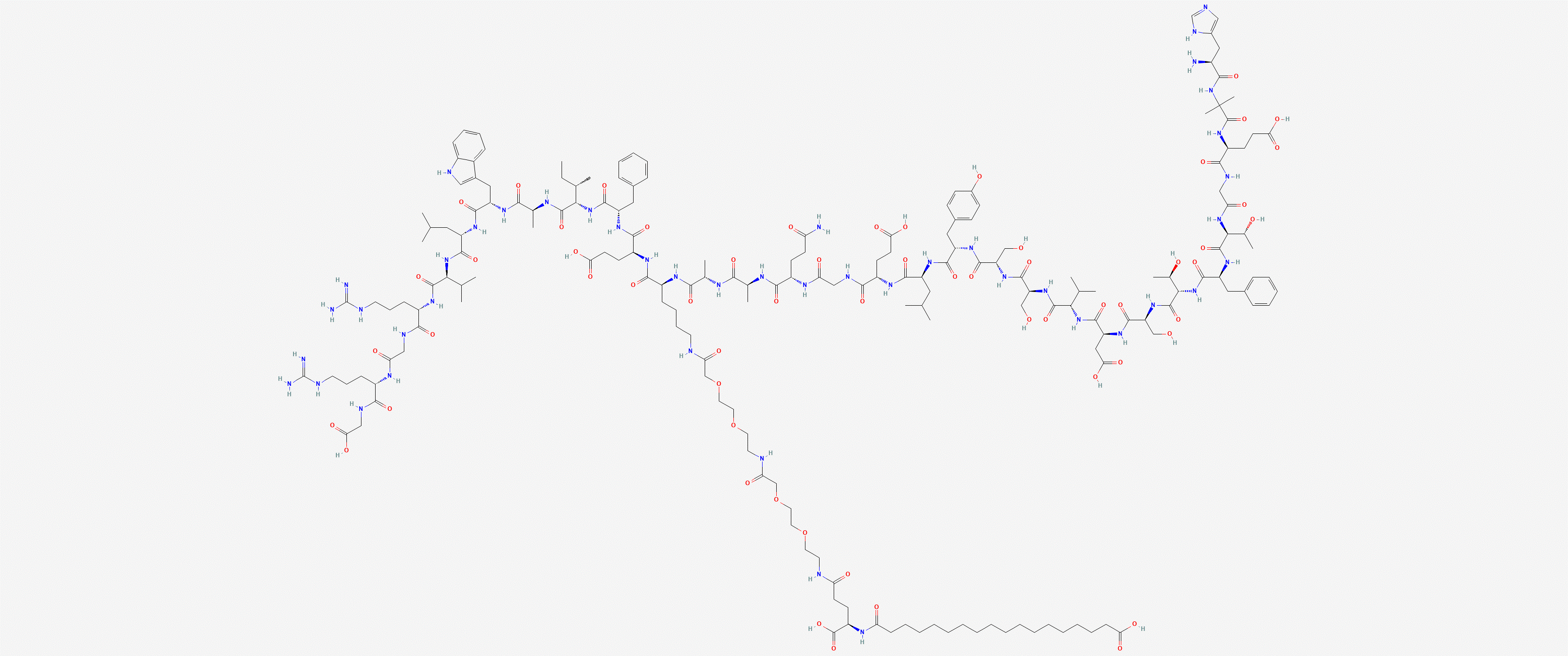
Sequence: HXEGTFTSDVSSYLEGQAAK-OH.steric diacid-EFIAWLVRGRG
Molecular Formula: C187H291N45O59
Molecular Weight: 4113.64 g/mol
PubChem CID: 56843331
CAS Number: 910463-68-2
Synonyms: Semaglutide, Oxempic, Rybelsus, NN9535
Perhaps the most important effect that GLP-1 has, according to Dr. Holst, is referred to as the “incretin effect.” Incretins are a group of metabolic hormones, released by the GI tract, that cause a decrease in blood glucose (sugar) levels. GLP-1 has been shown to be one of the two most important hormones (the other being GIP) to stimulate the incretin effect in rodent models. Though GIP circulates at levels roughly 10 times higher than that of GLP-1, there is evidence that GLP-1 is the more potent of the two molecules, particularly when levels of blood glucose are quite high.
A GLP-1 receptor has been identified on the surface of pancreatic beta cells, making it clear that GLP-1 directly stimulates the exocytosis of insulin from the pancreas. When combined with sulfonylurea drugs, GLP-1 has been shown to boost insulin secretion enough to cause mild hypoglycemia in up to 40% of subjects[1]. Of course, increased insulin secretion is associated with a number of trophic effects including increased protein synthesis, reduction in the breakdown of protein, and increased uptake of amino acids by skeletal muscle.
Research in animal models suggests that GLP-1 can stimulate the growth and proliferation of pancreatic beta cells and that it may stimulate the differentiation of new beta cells form progenitors in the pancreatic duct epithelium. Research has also shown that GLP-1 inhibits beta cell apoptosis[1]. Taken in sum, these effects tip the usual balance of beta cell growth and death toward growth, suggesting that the peptide may be useful in treating diabetes and in protecting the pancreas against insult that harms beta cells.
In one particularly compelling trial, GLP-1 was shown to inhibit the death of beta cells caused by enhanced levels of inflammatory cytokines. In fact, mouse models of type 1 diabetes have revealed that GLP-1 protects islet cells from destruction and may, in fact, be a useful means of preventing onset of the type 1 diabetes[2].
Research in mouse models suggests that administration of GLP-1, and its similar cousin GLP-1, into the brains of mice can reduce the drive to eat and inhibit food intake[3]. It appears that GLP-1 may actually enhance feelings of satiety, helping individuals to feel fuller and reducing hunger indirectly. Recent clinical studies have shown in mice that twice daily administration of GLP-1 receptor agonists cause gradual, linear weight loss. Over a long period, this weight loss is associated with significant improvement in cardiovascular risk factors and a reduction in hemoglobin A1C levels, the latter of these being a proxy marker for the severity of diabetes and the quality of blood sugar control attained via treatment[4].
It is now know that GLP-1 receptors are distributed throughout the heart and act to improve cardiac function in certain settings by boosting heart rate and reducing left ventricular end-diastolic pressure[5]. The latter may not seem like much, but increased LV end-diastolic pressure is associated with LV hypertrophy, cardiac remodeling, and eventual heart failure.
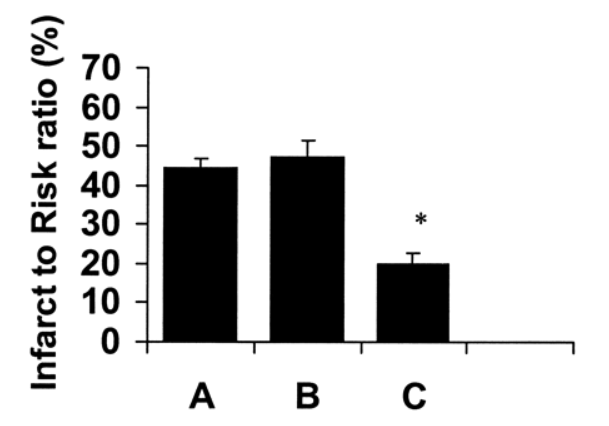
Recent evidence has even suggested that GLP-1 could play role in decreasing the overall damaged caused by a heart attack. It appears that the peptide improves cardiac muscle glucose uptake, thereby helping struggling ischemic heart muscle cells to get the nutrition they need to continue functioning and avoid programmed cell death. The increase in glucose uptake in these cells appears to independent of insulin[6].
Large infusions of GLP-1 into dogs have been shown to improve LV performance and reduce systemic vascular resistance. The latter effect can help to reduce blood pressure and ease strain on the heart as a result[7]. This, in turn, can help to reduce the long-term consequences of high blood pressure such as LV remodeling, vascular thickening, and heart failure. According to Dr. Holst, administration of GLP-1 following cardiac injury has “constantly increased myocardial performance both in experimental animal models and in patients.”
There is some evidence to suggest that GLP-1 can improve learning and help to protect neurons against neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease. In one study, GLP-1 was shown to enhance associative and spatial learning in mice and even to improve learning deficits in mice with specific gene defects. In rats that over-express the GLP-1 receptor in certain regions of the brain, learning and memory are both significantly better than in their normal controls[8].
Additional research in mice has shown that GLP-1 can help to protect against excitotoxic neuron damage, completely protecting rat models of neurodegeneration against glutamate-induced apoptosis. The peptide can even stimulate neurite outgrowth in cultured cells. Researchers are hopeful that additional research on GLP-1 will reveal how it might be used to halt or reverse certain neurodegenerative diseases[9].
Interestingly, GLP-1 and its analogue exendin-4 have been shown in mouse models to reduce levels of amyloid-beta in the brain as well as the beta-amyloid precursor protein found in neurons. Amyloid beta is the primary component of the plaques observed in Alzheimer’s disease, plaques which, while not necessarily known to be causative, are associated with the severity of the disease. It remains to be seen if preventing amyloid beta accumulation can protect against the effects of Alzheimer’s disease, but this research is, at the very least, a tantalizing clue as to how scientists my intervene in the progression of mild cognitive impairment to full Alzheimer’s disease[10].
GLP-1 exhibits minimal to moderate side effects, low oral and excellent subcutaneous bioavailability in mice. Per kg dosage in mice does not scale to humans. GLP-1 for sale at
The above literature was researched, edited and organized by Dr. Logan, M.D. Dr. Logan holds a doctorate degree from Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine and a B.S. in molecular biology.
In 1986 Professor Jens Juul Holst discovered the GLP-1 hormone in connection with his work on stomach ulcer surgery. Since the discovery, Novo Nordisk have used the research to successfully develop products to treat diabetes and obesity. The hormone GLP-1 can be used to regulate blood sugar levels and satiety. Not only has it made treatment of obesity and diabetes possible, it has also proven useful preventatively through early diagnosis for citizens who are at risk of developing diabetes and obesity. In 2015, Jens Juul Holst received the prestigious international Fernström prize for his research on GLP-1. He is one of the most cited researchers in Europe, with over 1,200 published articles and citations in over 3,500 articles annually.
Professor Jens Juul Holst is being referenced as one of the leading scientists involved in the research and development of GLP-1. In no way is this doctor/scientist endorsing or advocating the purchase, sale, or use of this product for any reason. There is no affiliation or relationship, implied or otherwise, between
ALL ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR INFORMATIONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
The products offered on this website are furnished for in-vitro studies only. In-vitro studies (Latin: in glass) are performed outside of the body. These products are not medicines or drugs and have not been approved by the FDA to prevent, treat or cure any medical condition, ailment or disease. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law.
PeptideGurus is a leading supplier of American-made research peptides, offering top-quality products at competitive prices. With a focus on excellence and customer service, they ensure a secure and convenient ordering process with global shipping.
CONTACT