


Categories: Peptide Finished product, Peptides and Their Dosages
Free (1) 30 ml Bacteriostatic Water
with qualified orders over $500 USD.
(excludes capsule products, cosmetic peptides, promo codes and shipping)
PEGylated Mechano-Growth Factor is a modified form of MGF, itself a modified form of IGF-1. Research has shown it to lower cholesterol and total body fat, boost immune function, and improve rates of wound healing.
Product Usage: This PRODUCT IS INTENDED AS A RESEARCH CHEMICAL ONLY. This designation allows the use of research chemicals strictly for in vitro testing and laboratory experimentation only. All product information available on this website is for educational purposes only. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law. This product should only be handled by licensed, qualified professionals. This product is not a drug, food, or cosmetic and may not be misbranded, misused or mislabled as a drug, food or cosmetic.
Pegylated Mechano-growth factor (PEG-MGF) is a truncated and slightly altered form of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). Research shows that it stimulates myoblast (muscle cell) proliferation and differentiation. It has also been explored in research focused on increasing endurance, boosting the function of the immune system, lowering cholesterol, and reducing total body fat. There is also some evidence to suggest that PEG-MGF improves immune function related to healing and could therefore less the time it takes for wounds to heal.
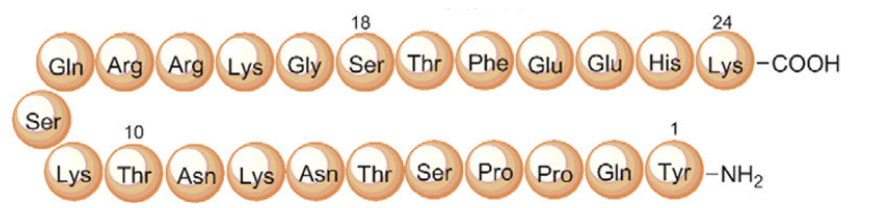
Pegylation is a process of attaching polyethylene glycol to another chemical compound. It is often done to reduce the body’s natural immune reaction to an agent or, as in the case of PEG-MGF, to increase the half-life of the compound in the blood by reducing clearance in the kidneys. Pegylation is common, safe, and has a number of advantages. PEG-MGF was developed because MGF has a very short half-life in blood. Though it persists for longer periods of time in muscle tissue, MGF administered exogenously has a short half-life because it passes through the blood stream first unless it is injected directly into muscle tissue. PEG-MGF helps to offset this particular disadvantage.
Injuries to muscle are common in sports and include everything from strains and sprains to outright avulsion injuries. In many cases, these types of injury require surgical repair. Regardless of the treatment, however, recover tends to be long and results are not always perfect. Research in a mouse model of muscle injury, however, suggests that MGF injected directly into muscle protects the cells by decreasing expression of certain inflammatory hormones, and reducing oxidative stress[1].
Similar research by Sun et. al. shows that MGF modulates muscle inflammation and improves the recruitment of macrophages and neutrophils to the site of injury[2]. Both studies are based on the previous knowledge that exercise-induced muscle damage stimulates the release of IGF-1Ea and IGF-1Eb, both of which are closely related to MGF[3].
Studies carried out by an international group of endocrinology researchers reveals that MGF stimulates the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor just as much as IGF-1[4]. Stimulation of this receptor has been linked to decreased aging, increased lean body mass, and improved energy homeostasis in humans. This function suggests that PEG-MGF can produce effects similar to IGF-1 leading to improved muscle repair, enhanced fat metabolism, and overall increases in lean body mass.
Research in mice also shows a 25% increase in mean muscle fiber size when MGF is administered to mice that are exercising[5]. In this study, the MGF was injected directly into the muscle, something that authors Goldspink and Jakeman point out as a serious limitation as the protein would have to be injected into every muscle in which hypertrophy is to be optimized. PEG-MGF solves this particular problem by increasing the plasma half-life of MGF and allowing it to be administered via a single intravenous injection rather than multiple intramuscular injections.
Research carried out in the department of bioengineering at the University of Illinois shows that MGF inhibits the programmed cell death that cardiac muscle cells undergo following hypoxia. Furthermore, the peptide appears to recruit cardiac stem cells to the site of injury and may therefore help in regeneration and healing following heart attack. Rats in the study were administered MGF within eight hours of hypoxia and showed less cell death and greater stem cell recruitment compared to controls that did not receive MGF[6]. Dr. Doroudian, lead author of the research, believes that using nanorods to deliver MDF in the setting of heart damage may be an effective way to provide localized, long-term therapy of the bioactive peptide to areas of injury.
Similar research indicates that localized delivery of MGF shows that it can improve cardiac function following heart attack by reducing pathologic hypertrophy. Rats in the study that were treated with PEG-MGF showed better hemodynamics and less cardiac remodeling than untreated rats[7]. Carpenter et. al. have similarly shown that MGF injected in the setting of acute myocardial infarction can reduce cardiomyocyte injury by as much as 35%.
Research in rabbits indicates that PEG-MGF can increase the rate of bone repair by boosting the proliferation of osteoblasts, the cells that mineralize bone. Rabbits treated with high doses of MGF showed the same level of healing at four weeks that was seen in controls at six weeks[8]. There is hope that this technique can help scientists learn how to promote bone healing and reduce time that people must spend immobilized to allow for healing.
Research indicates that MGF can improve the function of chondrocytes, the cells primarily responsible for cartilage health and deposition. Research in mice shows that MGF enhances the migration of chondrocytes from bone, where the cells develop, into cartilage where they have an effect[9]. This is a perfect setting for PEG-MGF because it could be injected into compromised joint spaces and would remain for long periods of time. A single injection could, in theory, be useful for weeks or even months whereas standard MGF has an effect limited to minutes or perhaps hours.
Research in cell cultures of human periodontal ligament cells indicates that PEG-MGF can improve osteogenic differentiation and boost expression of MMP-1 and MMP-2[10]. These factors act to improve repair of the ligaments that attach the tooth to bone and may offer an alternative to too extractions and implants, allowing people to keep their natural teeth after injury. There is even speculation that PEG-MGF may make it possible to save damaged or avulsed teeth after they are surgically re-implanted.
Alexander Walker, Editorial Assistant at BioMed Central, has recently reviewed a study exploring the long-term effects of increased levels of MGF in the brain and central nervous system. The study reveals that higher levels of MGF help to reduce the effects of age-related neuron degeneration, resulting in mice that retain their cognitive functions and operate a peak cognitive performance longer into old age. According to Walker, “the efficacy of MGF in the brain is age-dependent” as mice in the study had improved results both initially and over the long-term if MGF overexpression occurred earlier in life[11].
Treatment with MGF has also been shown to improve muscle weakness and reduce the loss of motor-neurons in mouse models of ALS[12]. According to Dluzniewska et al., MGF is naturally expressed in the brain following hypoxic injury and is over-expressed in regions of the brain where neuron regeneration is greatest. By administering exogenous MGF, it may be possible to reduce the impact of a number of neurological diseases, no
PEG-MGF exhibits minimal side effects, low oral and excellent subcutaneous bioavailability in mice. Per kg dosage in mice does not scale to humans. PEG-MGF for sale at
The above literature was researched, edited and organized by Dr. Logan, M.D. Dr. Logan holds a doctorate degree from Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine and a B.S. in molecular biology.
Paul Goldspink, PhD is the Principal Investigator and Associate Professor at the Department of Physiology within the Medical College of Wisconsin. The research in Dr. Goldspink’s laboratory is focused on understanding the actions of IGF-1 isoforms in the heart and other tissues. We are investigating the role of IGF-1 isoforms in response to stresses such a mechanical overload, hypoxia, oxidative stress and age in the heart. We have focused on a particular isoform called Mechano-Growth Factor (MGF), which plays a protective role in preventing cell death, preserving contractility and preventing pathologic hypertrophy of the heart following myocardial infarction. We are currently investigating the underlying mechanisms utilizing peptide analogs derived from the E-domain region of MGF which serve as allosteric modulators of excitation-transcription pathways in muscle. Through collaborations we have been able to exploit our findings by developing a technology that combines a microscopic physical scaffold to deliver peptide therapeutics, with the goal of improving cardiac function during the progression of heart failure by using implantable cell-sized “biomimetic devices”. The development of these intelligent drug delivery platforms which we have recently employed in the heart, also have applicability of other tissues and disease states.
Paul Goldspink, PhD is being referenced as one of the leading scientists involved in the research and development of PEG-MGF. In no way is this doctor/scientist endorsing or advocating the purchase, sale, or use of this product for any reason. There is no affiliation or relationship, implied or otherwise, between
ALL ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR INFORMATONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
The products offered on this website are furnished for in-vitro studies only. In-vitro studies (Latin: in glass) are performed outside of the body. These products are not medicines or drugs and have not been approved by the FDA to prevent, treat or cure any medical condition, ailment or disease. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law.
PeptideGurus is a leading supplier of American-made research peptides, offering top-quality products at competitive prices. With a focus on excellence and customer service, they ensure a secure and convenient ordering process with global shipping.
CONTACT