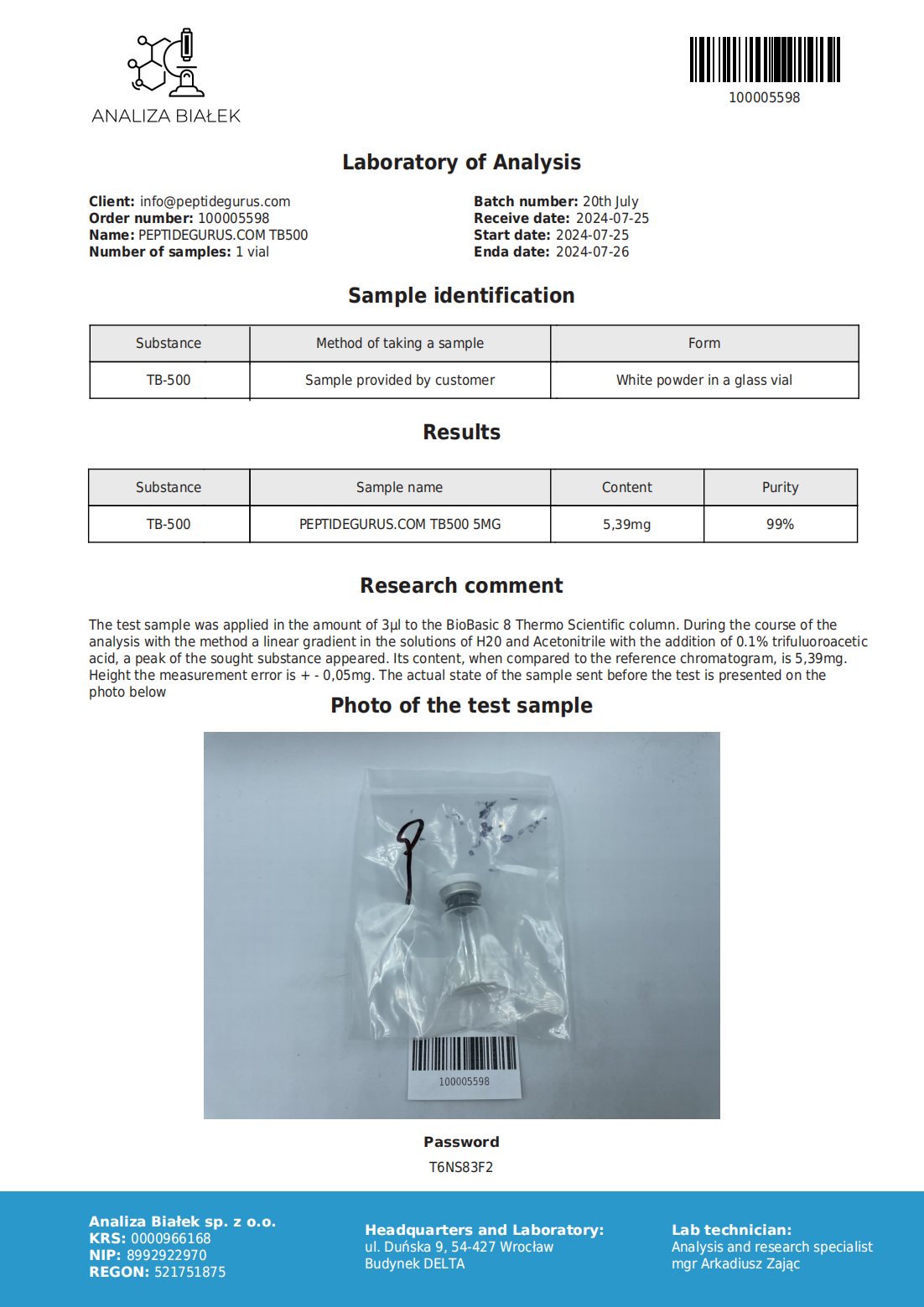
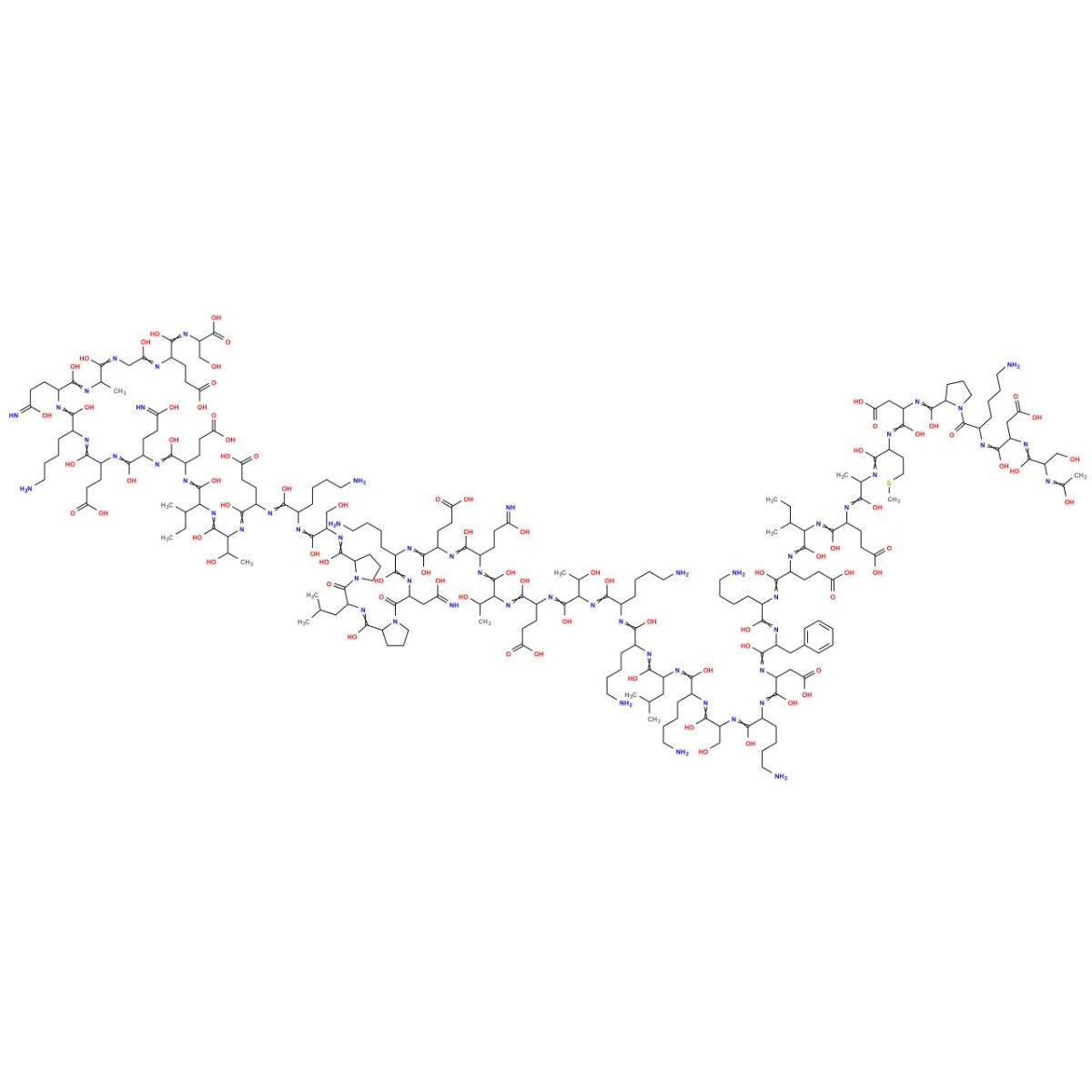
TB-500 (timosina beta-4) es un 43 secuencia peptídica de aminoácidos. En modelos animales, Se ha demostrado que la timosina Beta-4 mejora el crecimiento de los vasos sanguíneos., regular la cicatrización de heridas, disminuir la inflamación, y reducir el daño oxidativo en el corazón y el sistema nervioso central. La timosina-beta-4 tiene un papel en la protección., reparación de tejidos, regeneración y remodelación de tejidos lesionados o dañados. También es de interés activo en la investigación antienvejecimiento..
Gratis (1) 30 ml de agua bacteriostática
con pedidos calificados sobre $500 Dólar estadounidense.
(excluye productos en cápsulas, péptidos cosméticos, códigos promocionales y envío)
TB-500 (timosina beta-4) es un 43 secuencia peptídica de aminoácidos. En modelos animales, Se ha demostrado que la timosina Beta-4 mejora el crecimiento de los vasos sanguíneos., regular la cicatrización de heridas, disminuir la inflamación, y reducir el daño oxidativo en el corazón y el sistema nervioso central. La timosina-beta-4 tiene un papel en la protección., reparación de tejidos, regeneración y remodelación de tejidos lesionados o dañados. También es de interés activo en la investigación antienvejecimiento..
Uso del producto: Este PRODUCTO ESTÁ DISEÑADO ÚNICAMENTE COMO QUÍMICO DE INVESTIGACIÓN. Esta designación permite el uso de productos químicos de investigación estrictamente para pruebas in vitro y experimentación de laboratorio únicamente.. Toda la información del producto disponible en este sitio web es solo para fines educativos.. La introducción corporal de cualquier tipo en personas o animales está estrictamente prohibida por la ley.. Este producto sólo debe ser manipulado por personal autorizado., profesionales cualificados. Este producto no es un medicamento., alimento, o cosmético y no puede estar mal etiquetado, mal utilizado o mal etiquetado como droga, comida o cosmética.
What Is TB-500?
TB-500 is a 43 amino acid synthetic analogue of thymosin beta-4 (TB-4), which is found naturally in nearly all mammalian cells. TB-500 is known for its effects on actin protein, migración celular, y curación de heridas. TB-500 has been shown in animal models and in vitro studies to improve blood vessel growth, accelerate wound healing, disminuir la inflamación, and promote extracellular matrix production. The peptide is under current investigation for its ability to reduce oxidative stress in spinal cord injury, improve recovery following heart attack, and for its many anti-aging effects.
TB-500 Mechanism of Action
TB-500 is the active domain of TB-4, which has a primary role as an actin binding protein. Actin is a critical component of cell structure and makes up microfilaments. Microfilaments are responsible for giving cells their shape, protecting the integrity of cell membranes, allowing cells to move/migrate, and certain steps in cellular reproduction. Actin is also one of the primary components of muscle protein. Without actin, muscles could not contract. Actin binding proteins, like TB-4, sequester actin monomers, the individual units of actin, so that they are protected from degradation and are available for polymerization into microfilaments when needed.
TB-500 (timosina beta-4) Peptide Sequence
TB-500 Research
1. TB-500 and Neurologic Function
Research in rats has found that TB-500 encourages central and peripheral nervous system tissues to undergo repair and remodeling following injury. Though the exact mechanism has yet to be elucidated, the research indicates that TB-500 activates the cells that support neurons. These cells, called oligodendrocytes, keep neurons healthy[1]. Boosting their activity actually improves blood vessel and neuron growth in brain regions that have been damaged, a significant laboratory result that is reflected in clinically significant improvements in behavior, motor control, and cognitive measurements[2].
Recent research shows that TB-500 can reduce oxidative stress following spinal cord injury and help transplanted neural stem/progenitor cells (NSPCs) to survive long enough to enhance spinal regeneration[3]. These findings could make TB-500 and other TB-4 derivatives of great use in treating severe spinal cord injury. TB-550 may offer critical insight into spinal recovery that allows paralyzed individuals to regain use of affected body regions.
2. TB-500 and Blood Vessel Growth
TB-500 and TB-4 are potent stimulators of VEGF expression. VEGF is an important signaling molecule in the growth of capillaries (small blood vessels), which are critical to everything from wound healing to hair growth[4]. It is thought that the role of TB-500 is more complicated than this, sin embargo. Scientists speculate that the peptide likely underpins a number of steps in the process of blood vessel growth include extracellular matrix remodeling, vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, and the transition of more primitive mesenchymal tissue to the specialized endothelial tissue that lines blood vessels. This speculation is valid because loss of TB-4 has been shown to interfere with blood vessel growth and stability while exogenous administration improves capillary formation and the recruitment of pericytes following injury[4].
3. TB-500 and Hair Growth
The discovery that TB-500 improves hair growth happened by accident. When mice that were genetically deficient in TB-4 were shaved for laboratory experiments, it was observed that their hair grew back much slower than wild-type mice. When these same scientists investigated hair growth in mice that were genetically modified to produce increased levels of TB-4, they found that their hair grew back much faster than normal. Under the microscope, these mice show increased numbers of hair shafts and grouped hair follicles[5].
4. TB-500 and Antibiotic Synergy
Multi-drug resistance is becoming increasingly common in a number of infections, rendering current therapy ineffective. Desafortunadamente, there are very few new antibiotics in the pipeline and the process of drug development can take upwards of twenty years on average. A recent study on the effects of TB-4 and its adjuvants, sin embargo, provides some hope. Studies of mice suffering from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection of the eye have found that TB-4 combined with ciprofloxacin, a standard antibiotic for treating Pseudomonas aeruginosa, increases the effects of the antibiotic, improves healing, reduces inflammation, and promotes faster recovery. The results of just five days of combined therapy showed decreased numbers of colony forming units (CFUs), decreased neutrophil (a type of white blood cell) count, and decreased levels of inflammatory reactive oxygen species[6]. This is the first study to demonstrate that TB-500 and similar peptides might be used to promote and enhance the effects of antibiotics.
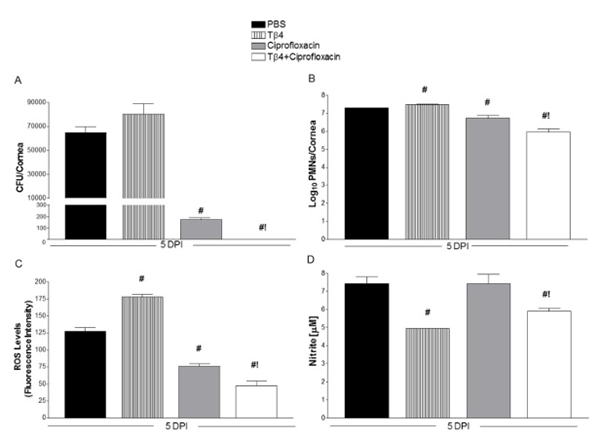
B. Shows number of neutrophils in the corneas of treated mice, an indication of inflammation.
C. Measure of reactive oxygen species in corneas of mice after 5 days of treatment.
D. Nitrate levels from corneal lysates.
Fuente: PubMed
5. TB-500 and Cardiovascular Health
Two decades of research have shown that TB-4 and its derivatives have a number of beneficial effects in the cardiovascular and renal systems. The exact mechanisms of these positive contributions are not clearly understood, sin embargo. Research suggests that the benefits are actually due to several mechanisms. Primero, TB-500 promotes the growth of collateral blood vessels, which is useful both as a preventative and in restoring function following disease. Segundo, TB-500 encourage endothelial cell migration and myocycte survival following a heart attack. Finalmente, it appears that TB-500 works in concert with other natural signaling molecules to reduce inflammation and reduce fibrosis (scar formation)[7].
Recientemente, research into hydrogels containing a combination of collagen and TB-4 has shown the peptide promotes angiogenesis and epicardial heart cell migration, thus boosting rates of recovering following ischemia and helping to prevent long-term complications by reducing scarring[8].
6. TB-500 and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Progress in finding a treatment for neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and prion disease has been slow at best. A recent study into the effects of TB-4 on the ability of the immune system to deal with prion protein has shown that the peptide enhances autophagy[9]. Autophagy is the central nervous system’s primary protective mechanism against neurodegenerative diseases. The ability of TB-4 to enhance this natural immunity is the first progression toward real treatment of these debilitating diseases in a long time.
7. TB-500 Has Wide Application
TB-500 due to its fundamental role in cell structure and function can affect a number of different body tissues. This has resulted in a wide and varied field of research into the effects of this peptide. From treating heart and neurological disease to enhancing the effects of antibiotics, TB-500 is one of the hottest peptides in research today and will likely remain one of the most heavily investigated peptides for the foreseeable future.
TB-500 exhibits minimal side effects, baja biodisponibilidad oral y excelente subcutánea en ratones. La dosis por kg en ratones no se aplica a los humanos. TB-500 for sale at
Autor del artículo
La literatura anterior fue investigada, editado y organizado por el Dr.. logan, MARYLAND. Dr. Logan tiene un doctorado de Facultad de Medicina de la Universidad Case Western Reserve y una licenciatura. en biología molecular.
Autor de revista científica
Alan L.. Goldstein, Maryland, Alan L.. Goldstein es profesor y Catharine B. & William McCormick Presidente del departamento de Bioquímica y Biología Molecular de la Facultad de Medicina y Ciencias de la Salud de la Universidad George Washington, donde ha servido desde 1978. timosinas fueron descubiertos a mediados de la década de 1960, cuando Allan Goldstein del Laboratorio de Abraham White en la Facultad de Medicina Albert Einstein de Nueva York estudió el papel del timo en el desarrollo del sistema inmunológico de los vertebrados. Es una autoridad de renombre mundial sobre la glándula del timo y el funcionamiento del sistema inmunitario, y codescubridor de las timosinas. Dr. Goldstein es autor de más de 400 artículos científicos en revistas profesionales, el inventor en más de 15 A NOSOTROS. Patentes, y editor de varios libros en los campos de la bioquímica., biomedicina, inmunología y neurociencia. Forma parte de los consejos editoriales de numerosas revistas científicas y médicas y ha sido consultor de muchas organizaciones de investigación en la industria y el gobierno.; cofundador del Instituto de Estudios Avanzados en Envejecimiento y Medicina Geriátrica, un instituto educativo y de investigación sin fines de lucro; miembro del Patronato del Instituto de Vacunas Albert Sabin; y se desempeña como presidente de la junta directiva de RegeneRx Biopharmaceuticals. Dr. Goldstein recibió su B.S.. del Colegio Wagner de 1959 y su MS. y doctorado. de la Universidad de Rutgers en 1964. Se desempeñó como miembro de la facultad de la Facultad de Medicina Albert Einstein de 1964 a 1972, y se mudó a la Rama Médica de la Universidad de Texas en Galveston en 1972 como profesor y director de la división de Bioquímica.
Alan L.. Goldstein, MD is being referenced as one of the leading scientists involved in the research and development of TB-500 and other Thymosins. De ninguna manera este médico/científico respalda o defiende la compra, venta, o uso de este producto por cualquier motivo. No hay afiliación o relación., implícito o no, entre
Citas referenciadas
- PAG. Cheng, F. Kuang, h. zhang, GRAMO. Ju, y j. Wang, “Beneficial effects of thymosin β4 on spinal cord injury in the rat,”Neurofarmacología, volumen. 85, páginas. 408–416, Oct. 2014. [PubMed]
- METRO. Chopp and Z. GRAMO. zhang, “Thymosin β4 as a restorative/regenerative therapy for neurological injury and neurodegenerative diseases,” Opinión de experto. biol. Ahí., volumen. 15 Suplemento 1, páginas. S9-12, 2015. [PubMed]
- h. li, Y. Wang, incógnita. Hu, B. Mamá, y h. zhang, “Thymosin beta 4 attenuates oxidative stress-induced injury of spinal cord-derived neural stem/progenitor cells through the TLR4/MyD88 pathway,” Gene, volumen. 707, páginas. 136–142, Puede 2019. [PubMed]
- k. norte. Dubé and N. Smart, “Thymosin β4 and the vasculature: multiple roles in development, repair and protection against disease,” Opinión de experto. biol. Ahí., volumen. 18, No. sup1, páginas. 131–139, 2018. [PubMed]
- D. Philp, S. St-Surin, H.-J. Cha, H.-S. Moon, h. k. Kleinman, y M. Elkin, “Thymosin beta 4 induces hair growth via stem cell migration and differentiation," Ana. norte. Y. Acad. Ciencia., volumen. 1112, páginas. 95–103, Sep. 2007. [PubMed]
- t. W.. Carion et al., “Thymosin Beta-4 and Ciprofloxacin Adjunctive Therapy Improves Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Induced Keratitis,” Cells, volumen. 7, No. 10, Sep. 2018. [PubMed]
- k. METRO. Kassem, S. Vaid, h. Peng, S. Sarkar, and N.-E. Rhaleb, “Tβ4-Ac-SDKP pathway: Any relevance for the cardiovascular system?,” Can. j. fisiol. Farmacéutico., páginas. 1–11, Mar. 2019. [PubMed]
- A. D. Shaghiera, PAG. Widiyanti, y h. Yusuf, “Synthesis and Characterization of Injectable Hydrogels with Varying Collagen–Chitosan–Thymosin β4 Composition for Myocardial Infarction Therapy," J.. Funct. Biomater., volumen. 9, No. 2, Mar. 2018. [PubMed]
- H.-J. Él, S. kim, y j. Kwon, “Thymosin beta 4-Induced Autophagy Increases Cholinergic Signaling in PrP (106-126)-Treated HT22 Cells,” Neurotox. Res., Dic. 2018. [PubMed]
- Canción, Ran & Choi, Hyun & Cual, Hyung-In & Yoo, Myung & Parque, Yong-Beom & kim, Kyoung. (2012). Association between serum thymosin β4 levels of rheumatoid arthritis patients and disease activity and response to therapy. Clinical rheumatology. 31. 1253-8. 10.1007/s10067-012-2011-7. [Puerta de investigación]
- Philp, D., et al. “Thymosin β4 Promotes Angiogenesis, Wound Healing, and Hair Follicle Development.” Mechanisms of Ageing and Development, volumen. 125, No. 2, Feb. 2004, páginas. 113–115, 10.1016/j.mad.2003.11.005. [PubMed]
TODOS LOS ARTÍCULOS E INFORMACIÓN DE PRODUCTOS PROPORCIONADOS EN ESTE SITIO WEB SON SÓLO PARA FINES INFORMATIVOS Y EDUCATIVOS.
Los productos ofrecidos en este sitio web se proporcionan únicamente para estudios in vitro.. Estudios in vitro (latín: en cristal) se realizan fuera del cuerpo. Estos productos no son medicamentos ni fármacos y no han sido aprobados por la FDA para prevenir, tratar o curar cualquier condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. La introducción corporal de cualquier tipo en personas o animales está estrictamente prohibida por la ley..