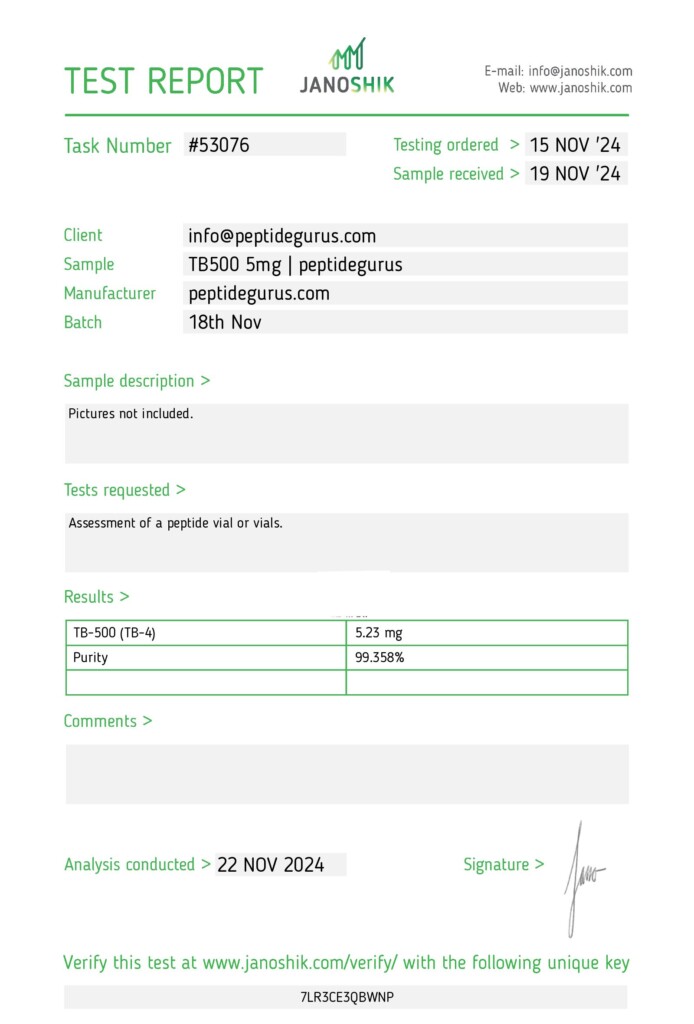



Categories: Peptide Finished product, Peptides and Their Dosages
TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4) is a 43 amino acid peptide sequence. In animal models, Thymosin Beta-4 has been shown to improve blood vessel growth, regulate wound healing, decrease inflammation, and reduce oxidative damage in the heart and central nervous system. Thymosin-beta-4 has a role in protection, tissue repair, regeneration and remodeling of injured or damaged tissues. It is also of active interest in anti-aging research.
Free (1) 30 ml Bacteriostatic Water
with qualified orders over $500 USD.
(excludes capsule products, cosmetic peptides, promo codes and shipping)
TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4) is a 43 amino acid peptide sequence. In animal models, Thymosin Beta-4 has been shown to improve blood vessel growth, regulate wound healing, decrease inflammation, and reduce oxidative damage in the heart and central nervous system. Thymosin-beta-4 has a role in protection, tissue repair, regeneration and remodeling of injured or damaged tissues. It is also of active interest in anti-aging research.
Product Usage: This PRODUCT IS INTENDED AS A RESEARCH CHEMICAL ONLY. This designation allows the use of research chemicals strictly for in vitro testing and laboratory experimentation only. All product information available on this website is for educational purposes only. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law. This product should only be handled by licensed, qualified professionals. This product is not a drug, food, or cosmetic and may not be misbranded, misused or mislabled as a drug, food or cosmetic.
TB-500 is a 43 amino acid synthetic analogue of thymosin beta-4 (TB-4), which is found naturally in nearly all mammalian cells. TB-500 is known for its effects on actin protein, cell migration, and wound healing. TB-500 has been shown in animal models and in vitro studies to improve blood vessel growth, accelerate wound healing, decrease inflammation, and promote extracellular matrix production. The peptide is under current investigation for its ability to reduce oxidative stress in spinal cord injury, improve recovery following heart attack, and for its many anti-aging effects.
TB-500 is the active domain of TB-4, which has a primary role as an actin binding protein. Actin is a critical component of cell structure and makes up microfilaments. Microfilaments are responsible for giving cells their shape, protecting the integrity of cell membranes, allowing cells to move/migrate, and certain steps in cellular reproduction. Actin is also one of the primary components of muscle protein. Without actin, muscles could not contract. Actin binding proteins, like TB-4, sequester actin monomers, the individual units of actin, so that they are protected from degradation and are available for polymerization into microfilaments when needed.
Research in rats has found that TB-500 encourages central and peripheral nervous system tissues to undergo repair and remodeling following injury. Though the exact mechanism has yet to be elucidated, the research indicates that TB-500 activates the cells that support neurons. These cells, called oligodendrocytes, keep neurons healthy[1]. Boosting their activity actually improves blood vessel and neuron growth in brain regions that have been damaged, a significant laboratory result that is reflected in clinically significant improvements in behavior, motor control, and cognitive measurements[2].
Recent research shows that TB-500 can reduce oxidative stress following spinal cord injury and help transplanted neural stem/progenitor cells (NSPCs) to survive long enough to enhance spinal regeneration[3]. These findings could make TB-500 and other TB-4 derivatives of great use in treating severe spinal cord injury. TB-550 may offer critical insight into spinal recovery that allows paralyzed individuals to regain use of affected body regions.
TB-500 and TB-4 are potent stimulators of VEGF expression. VEGF is an important signaling molecule in the growth of capillaries (small blood vessels), which are critical to everything from wound healing to hair growth[4]. It is thought that the role of TB-500 is more complicated than this, however. Scientists speculate that the peptide likely underpins a number of steps in the process of blood vessel growth include extracellular matrix remodeling, vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, and the transition of more primitive mesenchymal tissue to the specialized endothelial tissue that lines blood vessels. This speculation is valid because loss of TB-4 has been shown to interfere with blood vessel growth and stability while exogenous administration improves capillary formation and the recruitment of pericytes following injury[4].
The discovery that TB-500 improves hair growth happened by accident. When mice that were genetically deficient in TB-4 were shaved for laboratory experiments, it was observed that their hair grew back much slower than wild-type mice. When these same scientists investigated hair growth in mice that were genetically modified to produce increased levels of TB-4, they found that their hair grew back much faster than normal. Under the microscope, these mice show increased numbers of hair shafts and grouped hair follicles[5].
Multi-drug resistance is becoming increasingly common in a number of infections, rendering current therapy ineffective. Unfortunately, there are very few new antibiotics in the pipeline and the process of drug development can take upwards of twenty years on average. A recent study on the effects of TB-4 and its adjuvants, however, provides some hope. Studies of mice suffering from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection of the eye have found that TB-4 combined with ciprofloxacin, a standard antibiotic for treating Pseudomonas aeruginosa, increases the effects of the antibiotic, improves healing, reduces inflammation, and promotes faster recovery. The results of just five days of combined therapy showed decreased numbers of colony forming units (CFUs), decreased neutrophil (a type of white blood cell) count, and decreased levels of inflammatory reactive oxygen species[6]. This is the first study to demonstrate that TB-500 and similar peptides might be used to promote and enhance the effects of antibiotics.
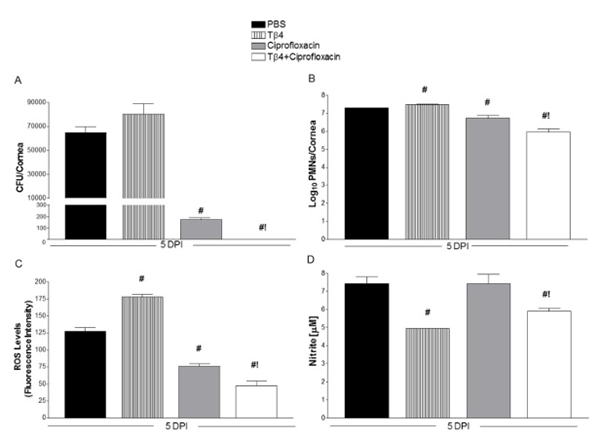
Two decades of research have shown that TB-4 and its derivatives have a number of beneficial effects in the cardiovascular and renal systems. The exact mechanisms of these positive contributions are not clearly understood, however. Research suggests that the benefits are actually due to several mechanisms. First, TB-500 promotes the growth of collateral blood vessels, which is useful both as a preventative and in restoring function following disease. Second, TB-500 encourage endothelial cell migration and myocycte survival following a heart attack. Finally, it appears that TB-500 works in concert with other natural signaling molecules to reduce inflammation and reduce fibrosis (scar formation)[7].
Recently, research into hydrogels containing a combination of collagen and TB-4 has shown the peptide promotes angiogenesis and epicardial heart cell migration, thus boosting rates of recovering following ischemia and helping to prevent long-term complications by reducing scarring[8].
Progress in finding a treatment for neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and prion disease has been slow at best. A recent study into the effects of TB-4 on the ability of the immune system to deal with prion protein has shown that the peptide enhances autophagy[9]. Autophagy is the central nervous system’s primary protective mechanism against neurodegenerative diseases. The ability of TB-4 to enhance this natural immunity is the first progression toward real treatment of these debilitating diseases in a long time.
TB-500 due to its fundamental role in cell structure and function can affect a number of different body tissues. This has resulted in a wide and varied field of research into the effects of this peptide. From treating heart and neurological disease to enhancing the effects of antibiotics, TB-500 is one of the hottest peptides in research today and will likely remain one of the most heavily investigated peptides for the foreseeable future.
TB-500 exhibits minimal side effects, low oral and excellent subcutaneous bioavailability in mice. Per kg dosage in mice does not scale to humans. TB-500 for sale at
The above literature was researched, edited and organized by Dr. Logan, M.D. Dr. Logan holds a doctorate degree from Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine and a B.S. in molecular biology.
Allan L. Goldstein, MD, Allan L. Goldstein is professor and Catharine B. & William McCormick Chair of the department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at The George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, where he has served since 1978. Thymosins were discovered in the mid 1960’s, when Allan Goldstein from the Laboratory of Abraham White at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York studied the role of the thymus in development of the vertebrate immune system. He is a world-renowned authority on the thymus gland and the workings of the immune system, and co-discoverer of the thymosins. Dr. Goldstein is the author of over 400 scientific articles in professional journals, the inventor on more than 15 U.S. Patents, and the editor of several books in the fields of biochemistry, biomedicine, immunology and neuro-science. He is on the editorial boards of numerous scientific and medical journals and has been a consultant to many re-search organizations in industry and government; co-founder of The Institute for Advanced Studies in Aging and Geriatric Medicine, a non-profit research and educational institute; a member of the Board of Trustees of the Albert Sabin Vaccine Institute; and serves as the Chairman of the Board of RegeneRx Biopharmaceuticals. Dr. Goldstein received his B.S. from Wagner College in 1959 and his M.S. and Ph.D. from Rutgers University in 1964. He served as a faculty member of the Albert Einstein College of Medicine from 1964 to 1972, and moved to the University of Texas Medical Branch in Galveston in 1972 as professor and director of the division of Biochemistry.
Allan L. Goldstein, MD is being referenced as one of the leading scientists involved in the research and development of TB-500 and other Thymosins. In no way is this doctor/scientist endorsing or advocating the purchase, sale, or use of this product for any reason. There is no affiliation or relationship, implied or otherwise, between
ALL ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR INFORMATIONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
The products offered on this website are furnished for in-vitro studies only. In-vitro studies (Latin: in glass) are performed outside of the body. These products are not medicines or drugs and have not been approved by the FDA to prevent, treat or cure any medical condition, ailment or disease. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law.
PeptideGurus is a leading supplier of American-made research peptides, offering top-quality products at competitive prices. With a focus on excellence and customer service, they ensure a secure and convenient ordering process with global shipping.
CONTACT