


Categories: Peptide Finished product, Peptides and Their Dosages
Free (1) 30 ml Bacteriostatic Water
with qualified orders over $500 USD.
(excludes capsule products, cosmetic peptides, promo codes and shipping)
FOX04-DRI (Retro-Inverso) is a synthetic, slightly modified version of the standard FOXO4 protein. The modification prolongs half-life of the protein and allows it to interfere with normal FOXO4 function. FOXO4-DRI has been shown in research to prevent normal FOXO4 binding to p53, thereby allowing for elimination of senescent cells, improved organ function, and younger tissue “biological age.” FOXO4-DRI impacts insulin signaling, cell cycle regulation, and oxidative stress signaling pathways. FOXO4-DRI is a cell penetrating peptide shown to selectively induce apoptosis of senescent cells thereby reversing effects of aging in animal studies.
Product Usage: This PRODUCT IS INTENDED AS A RESEARCH CHEMICAL ONLY. This designation allows the use of research chemicals strictly for in vitro testing and laboratory experimentation only. All product information available on this website is for educational purposes only. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law. This product should only be handled by licensed, qualified professionals. This product is not a drug, food, or cosmetic and may not be misbranded, misused or mislabled as a drug, food or cosmetic.
FOXO4 D-Retro-Inverso is identical to the protein product of the FOXO4 gene, but the normal L amino acids have been exchanged for D amino acids. The result is that FOXO4-DRI has reduced susceptibility to normal physiologic clearance mechanisms and thus remains in the body for longer periods of time. The modified protein is still capable, however, of affecting transcription and cellular pathways. In general, the FOXO4-DRI protein interferes with normal FOXO4 function.
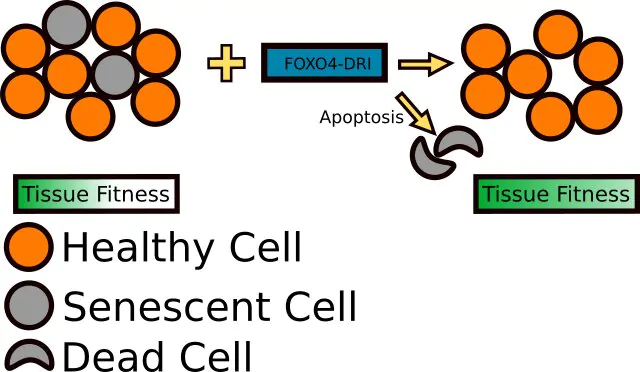
Of greatest interest in terms of aging and senescence is the ability of FOXO4-DRI to interfere with normal FOXO4 signaling in the cell cycle by preventing the binding of FOXO4 to p53. The p53 protein is an important regulator of progression through the cell cycle as well as programmed cell death (apoptosis). When FOXO4-DRI binds to p53, it prevents FOXO4 from binding and allows p53 to bind to DNA. This, in turn, allows the cell to continue through the process of apoptosis and die. Interestingly, FOXO4-DRI appears to only have this effect in senescent cells, cells that are no longer functional or are dysfunctional as a result of aging[2]. By targeting these dysfunctional cells, FOXO4-DRI helps to rid tissue of cells that are nothing but dead weight. This, in turn, allows for better tissue functioning and helps to stimulate growth and differentiation of younger, healthier cells. The net result is better biological function and thus a decrease in “biological age”.
DRI-Retro Inverso Peptides Explained Retro-inverso peptides are linear peptides whose amino acid sequence is reversed and the α-center chirality of the amino acid subunits is inverted as well. Usually, these types of peptides are designed by including D-amino acids in the reverse sequence to help maintain side chain topology similar to that of the original L-amino acid peptide and make them more resistant to proteolytic degradation. Other reported synonyms for these peptides in the scientific literature are: Retro-Inverso Peptides, All-D-Retro Peptides, Retro-Enantio Peptides, Retro-Inverso Analogs, Retro-Inverso Analogues, Retro-Inverso Derivatives, and Retro-Inverso Isomers. D-amino acids represent conformational mirror images of natural L-amino acids occurring in natural proteins present in biological systems. Peptides that contain D-amino acids have advantages over peptides that just contain L-amino acids. In general, these types of peptides are less susceptible to proteolytic degradation and have a longer effective time when used as pharmaceuticals. Furthermore, the insertion of D-amino acids in selected sequence regions as sequence blocks containing only D-amino acids or in-between L-amino acids allows the design of peptide-based drugs that are bioactive and possess increased bioavailability in addition to being resistant to proteolysis. Furthermore, if properly designed, retro-inverso peptides can have binding characteristics similar to L-peptides. Retro-inverso peptides are useful candidates for the study of protein-protein interactions by designing peptidomimetics that mimic the shape of peptide epitopes, protein-protein, or protein-peptide interfases. Retro-inverso-peptides are attractive alternatives to L-peptides used as pharmaceuticals. These of peptide have been reported to elicit lower immunogenic responses compared to L-peptides.
Source: Uniprot
Sequence: H-D-Leu-D-Thr-D-Leu-D-Arg-D-Lys-D-Glu-D-Pro-D-Ala-D-Ser-D-Glu-D-Ile-D-Ala-D-Gln-D-Ser-D-Ile-D-Leu-D-Glu-D-Ala-D-Tyr-D-Ser-D-Gln-D-Asn-D-Gly-D-Trp-D-Ala-D-Asn-D-Arg-D-Arg-D-Ser-D-Gly-D-Gly-D-Lys-D-Arg-D-Pro-D-Pro-D-Pro-D-Arg-D-Arg-D-Arg-D-Gln-D-Arg-D-Arg-D-Lys-D-Lys-D-Arg-D-Gly-OH
Molecular Formula: C228H388N86O64
Molecular Weight: 5358.05
Synonyms: Forkhead box protein O4, Proxofim, FOXO4a, AFX, AFX1, MLLT7
The relationship between FOXO4 and aging is complex and still not fully understood. There is, however, good evidence that helps to elucidate the mechanisms by which the protein has its effects. Research in the well-studied nematode C. elegans shows that FOXO4 affects insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling and thus cellular lifespan control, stress resistance, and gene regulation[3]. It also appears that FOXO4 interacts with the p53 protein to regulate the cell cycle.
Natural FOXO4 actually protects senescent cells by keeping p53, a regulator of the cell cycle, sequestered and unable to induce apoptosis. FOXO4-DRI disrupts the normal FOXO4/p53 mechanism and allows the latter protein to induce apoptosis in senescent cells. The result is an amelioration of senescence-associated loss of tissue homeostasis[4], [5]. Scientists refer to this as rejuvenation by therapeutic elimination of senescent cells. The process is not all that different from pruning a fruit tree. By removing dead and damaged branches (senescent cells), energy is redirected to healthier parts of the tree and thus to fruit production and growth. This same process happens at the organ and tissue level when cells that are contributing to overall unhealthy function are removed, allowing resources to be focused on healthy cells.
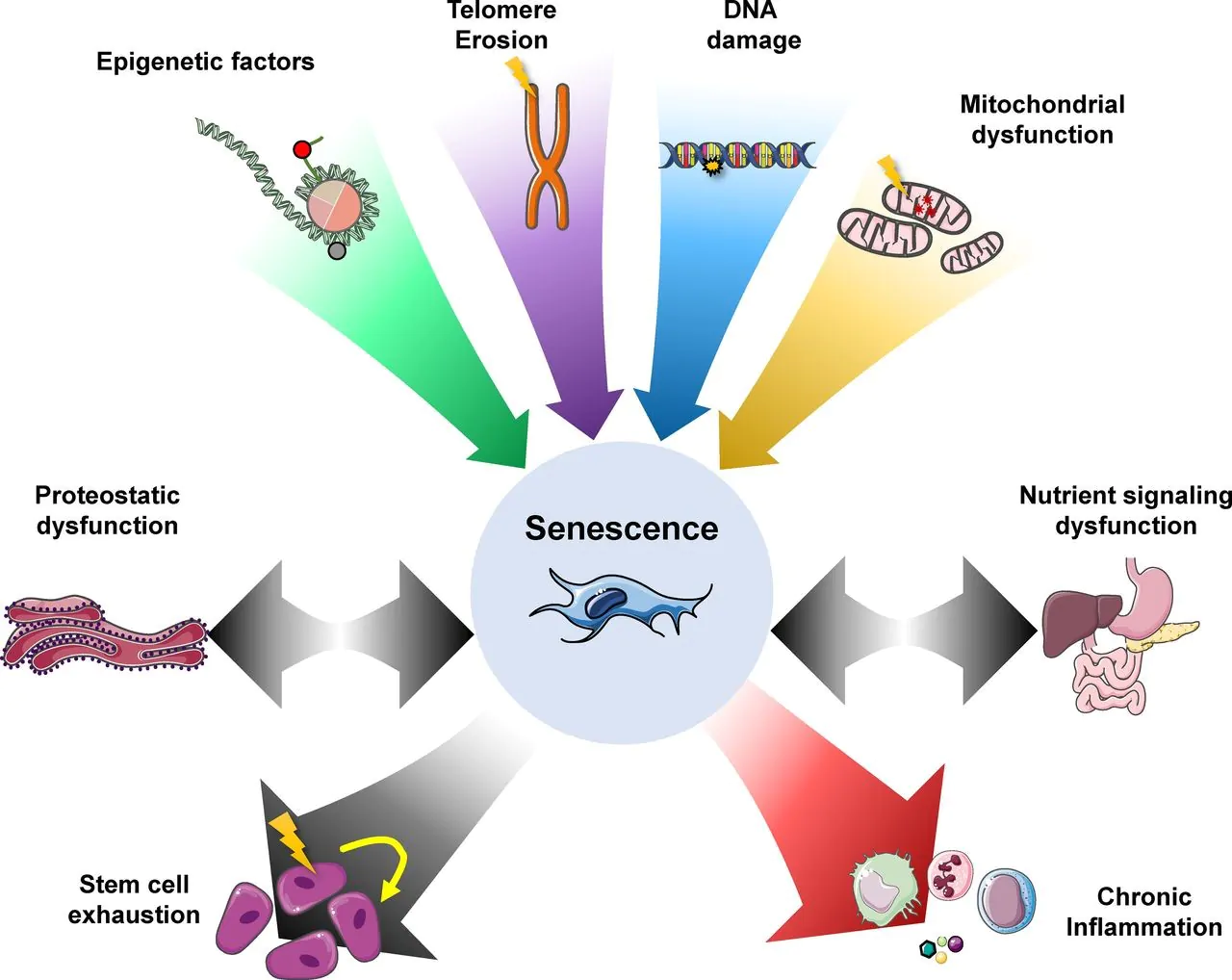
Source: Journal of Cell Biology
This image displays what factors contribute to senescence and what the outcomes are senescence are. Note that eliminating a senescent cell does not alleviate stem cell exhaustion, but may slow it down. It does, however, help to reduce chronic inflammation, a well-established driver of a number of conditions like cardiac disease, stroke, etc.
Irreparable damage, which is to say cellular damage that is beyond the ability of the body to fix, is one of the primary limitations to health span. Health span, the length of time during which an organism remains healthy and functioning optimally, is generally shorter than lifespan. A decline in healthspan manifests as aging. The ability to extend health span may not result in more years lived, but it can result in living out the years allotted to us in greater health and with better functioning. In mouse models, FOXO4 has been shown to improve health span in aged mice, leading to an increase in fitness, fur density, and renal functioning. The mice do not necessarily live longer, but they have greater health, even into old age, which translates into less disability and fewer age-related conditions like heart disease, musculoskeletal dysfunction, etc[2].
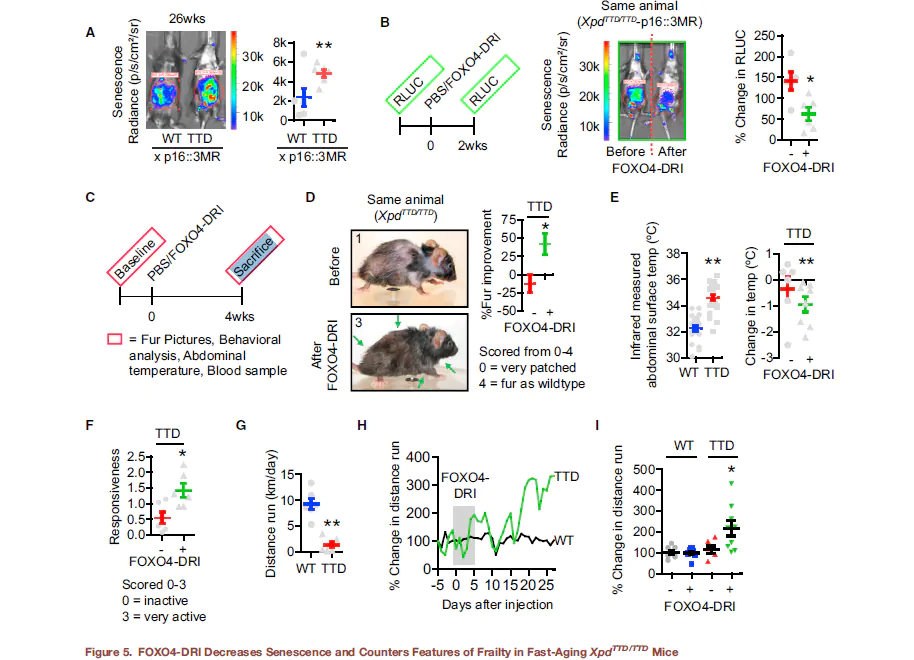
Images showing improved fitness, as indicated by fur density, in a mouse treated with FOXO4-DRI after subjected to chemotoxic agents used to model aging:
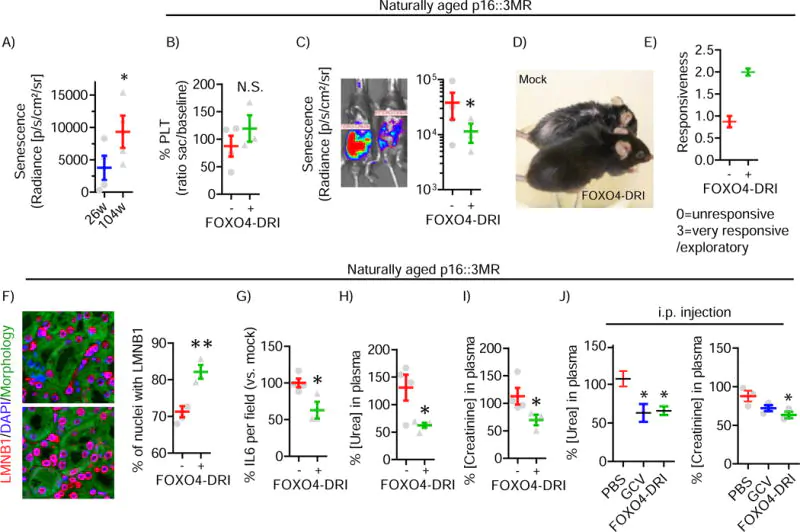
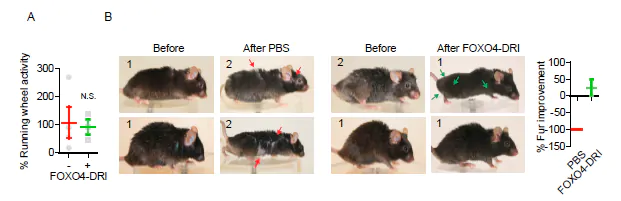
Source: Pubmed.
It has long been understood that FOXO proteins are important regulators of insulin signaling, but that they act downstream of the insulin itself as well as insulin-like growth factors. Research in animal models indicates that FOXO mediates that inhibitor effects of insulin and insulin-like growth factor on cell metabolism, growth, differentiation, oxidative stress, and more. Mutations in FOXO are connected to pathologic changes in insulin signaling and the development of metabolic disease as well as cancer. In diabetics, alterations of FOXO signaling leads to fasting hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia[6]. The latter is one of the most concerning aspects of diabetes as it leads to many of the complications of the disease such as kidney damage, stroke, heart attack, impaired wound healing, and more. The ability to regulate FOXO signaling in diabetes could provide for more targeted, more effective methods of preventing some of the serious complications of the disease. It is unclear how FOXO4-DRI affects insulin signaling, but it is thought that the protein can improve downstream effects of insulin by reducing fasting blood sugar levels.
Age is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. This risk appears to be mediated by declines in proteasome activity in the heart. Proteasomes are responsible for removing oxidized proteins and other proteins that the cell has marked as “damaged” or dysfunctional. Research in rats shows that age is inversely correlated with proteasome activity and thus increases in levels of damaged proteins within the heart[7].
FOXO proteins mediate autophagy and proteasome activity. Increases in FOXO4 levels lead to increases in proteasome activity and thus decreased levels of oxidation and protein damage within specific tissue. It may be possible that FOXO4-DRI or a variant of it can be used to boost the heart’s natural housekeeping functions and thus reduce age-related changes in cardiovascular function[8].
Age-related changes in cognitive function have a complex etiology. Even relatively common diseases, like Alzheimer’s disease, are not fully understood by the medical community. There is some evidence, however, to support the notion that changes in proteasome activity can lead to or exacerbate underlying neurodegenerative conditions. It isn’t clear if impaired proteasome activity is a primary cause or secondary contributor to diseases like Alzheimer’s disease, but impairment of the systems has been found in Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, Huntington’s, and Prion disease. There is also impairment of proteasome function in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS or Lou Gehrig’s disease) [9].
It appears that FOXO proteins are modified in the central nervous system, a finding that has led researchers to explore the idea that exogenous FOXO protein may be useful in treating or preventing neurodegenerative disorders. At the very least, there is hope that FOXO4-DRI and other modified FOXO proteins may be useful in slowing the relentless progression of neurodegenerative disorders [10].
FOXO4-DRI has been clearly demonstrated to boost apoptosis in cells that have become senescent, leading to improved tissue function and better overall health in animal models. It remains to be seen just how extensive the effects of FOXO4-DRI are, but there is hope that the protein can unlock insight into age-related conditions like dementia, heart disease, and general loss of function caused by cell senescence.
FOXO4-DRI exhibits minimal side effects, low oral and excellent subcutaneous bioavailability in mice. Per kg dosage in mice does not scale to humans. FOXO4-DRI for sale at
Peptide Gurus is limited to educational and scientific research only, not for human consumption. Only buy FOXO4-DRI if you are a licensed researcher.
The above literature was researched, edited and organized by Dr. Logan, M.D. Dr. Logan holds a doctorate degree from Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine and a B.S. in molecular biology.
The aim of Dr. Peter de Keizer’s group is to unravel the molecular mechanisms that cause cells to become senescent and to identify how these cells drive aging and age-related diseases. The role of senescence in late-stage therapy-resistant cancer is a major component of this research. The research has a strong translational component and a spearpoint of the group is to develop methods to target the deleterious effects of senescent and senescent-like cancer cells, for instance by eliminating them altogether. In 2004, Peter obtained his MSc in Biomolecular Science form Utrecht University. The final part of his training was performed at Harvard Medical School / Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, USA. Here, he focused on therapy-resistant Glioblastoma, the most lethal form of brain cancer, something which is now on of the focus areas of the group. In 2009, Peter obtained his PhD from UMC Utrecht on the regulation of FOXO proteins under conditions of stress and their role in tumor suppression.
Dr. Peter de Keizer is being referenced as one of the leading scientists involved in the research and development of FOXO4-DRI. In no way is this doctor/scientist endorsing or advocating the purchase, sale, or use of this product for any reason. There is no affiliation or relationship, implied or otherwise, between
Peptide Gurus and this doctor. The purpose of citing the doctor is to acknowledge, recognize, and credit the exhaustive research and development efforts conducted by the scientists studying this peptide. Dr. Peter de Keizer is listed in [2] under the referenced citations.
ALL ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR INFORMATIONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
The products offered on this website are furnished for in-vitro studies only. In-vitro studies (Latin: in glass) are performed outside of the body. These products are not medicines or drugs and have not been approved by the FDA to prevent, treat or cure any medical condition, ailment or disease. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law.
PeptideGurus is a leading supplier of American-made research peptides, offering top-quality products at competitive prices. With a focus on excellence and customer service, they ensure a secure and convenient ordering process with global shipping.
CONTACT