What is Melanotan 1?
Melanotano 1 is a syntetic analogue of alpha-melanotocyte stimulating hormone. lt isused clinically, in Europe, to prevent sun-related skin damage (es decir. phototoxicity) fromffering from erythropoietic protoporphyria. Though initiallyoccurring in people s!ss tanning agent, melanotan 1 has been found to have a number ofdeveloped as a sunlephysiologic effects onblood pressure, feeding behavior, central nervous system function,y más. The peptidis in phase 3 clinical trials for the treatment of polymorphose lighteruption and is in phase 2 clinical trials for the treatment of actinic keratosis (a specifictype of skin damageaused by the sun) and its more serious counterpart, squamous celcarcinoma.
Structure Melanotan 1
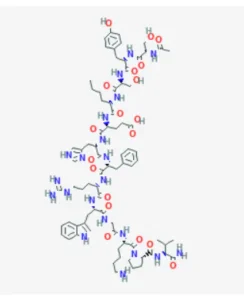
Secuencia:Ser-Tyr-Ser-Nle-Glu-His-D-Phe-Arg-Trp-Gly-Lys-Pro-Val
Fórmula molecular: CH.Nz1O1.
Peso molecular: 1646.874 g/mol
PubChem ClD: 16154396
Número CAS: 75921-69-6
Sinónimos: Afamelanotide, Scenesse, CUV1657, MT-1
How Does Melanotan 1 Work?
Melanotano 1 is very $imilar to naturally occurring alpha melanocyte stimulating hormone(alpha-MSH). Alpha-iSH is primarily known for its influence on melanocytes, the cells inible for pigmentation. This function is mediated via strong binding toskin and hair respons1.Alpha-MSH is a non-selective full agonist of melanocortinmelanocortin receptoreceptors and Melanotan 1 differs from alpha-MSH by a single amino acid and was actually firstSs tanning agent. Research into melanocortin receptors and their developed as a sunlelimited at the time and scientists quickly discovered that while effects was relativelyed cause pigmentation, it also increase sexual arousal, boostedmelanotan 1 did inde!appetite, and alteredaseline metabolism. Subsequent study of melanotan 1 and other melanocortin-bindingproteins helped scientists to better understand the melan ocortinsignaling system.
Melanotano 1 Investigación
Melanotano 1 Originally Designed for Sunless Tanning
MT-1 has been studied in phase 1 clinical trials for its effect on tanning in humans exposed to ultraviolet radiation. The research showed that subjects administered MT-1were 75% more likely to tan and 47% less likely to experience sunburn. Compared tocontrols, subjects given melanotan 1 required 50% less exposure to ultraviolet light toachieve eauivalent tanning, They also retained their tan for three weeks onger than thoseexposed only to UV light[1]. There is some thought among scientists that melanotan 1could be used to boost tanning in high UV settings to protect against sunburn and thelong-term effects of ultraviolet skin damage. This could be particularly useful in individualswith poor-tanning skin types (referred to as type l and type ll by the Fitzpatrick scale).
Research in individuals with variant Mc1 receptors shows that they are ess ikely to tanthan the average individual. Como resulta, administration of melanotan 1 in this settingincreases melanin density and tanning substantially, helping to protect people who do nottan well and are most in need of photoprotection[2]. These are individuals who get limitedbenefit from sunscreen and, in order to prevent skin cancer, must limit their sun exposurea great deal. This research could open pathways to better UV protection and reduce ratesof skin cancer substantially.
There is also interest in using melanotan 1 to treat vitiligo. A small phase 1 trial showedthat using melanotan 1 in conjunction with UVB light therapy stimulated both melaninproduction and the proliferation of the melanocytes that produce melanin. Nearly half oftreated patients showed improved pigmentation of vitiligo esions and a faster rate ofrepigmentation[3]. Research shows that combining melanotan 1 treatment with existinotreatment modalities of vitiligo produces synergistic effects and improved aestheticoutcomes in shorter periods of time[4], if successful in vitiligo treatment, there may beapplications for melanotan 1 treatment in the setting of hypopigmented scars, etc..
Actinic keratosis, also called solar keratosis, is a crusty scaly growth of skin caused byoverexposure to UV light. lt is considered a precancerous lesion that will eventually leadto squamous cell carcinoma (one type of skin cancer) if left untreated. There are morethan 400,000 cases every year. Though obvious lesions can be removed by adermatologist or surgeon, the vast majority are so small that they cannot be seen or evenfelt, Melanotano 1 is being investiaated as a possible first-line agent for treating theseinvisible lesions and for preventing their progression to full-blown skin cancer.
Melanotan-1 Research and Blood Pressure
Research in hypertensive (hipertensión) mice has revealed that melanotan 1 canprotect against high blood pressure without affecting animals that have normal bloodpressure[5]. This is important because current blood pressure medications can causehypotension, which can lead to loss of consciousness, ataque, infarto de miocardio, and moreThis side effect of blood pressure medications is more common in the elderly, thanks inpart to their labile physiology. The ability to regulate high blood pressure without causingsignificant lows makes melanotan 1 the perfect candidate for exploring further drugdevelopment.
Cognitive Decline, Alzheimer’s Disease, and Melanotan 1
Research in transgenic mice indicates that melanotan 1 may protect the brain against thekind of damage that leads to cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease. El estudio, whichused a mouse model of moderate Alzheimer’s disease (ANUNCIO), indicated that melanotan 1.even in minuscule doses, reduces the level of amyloid beta plaques in the brain, protectsneurons from death, and improves clinical measures of cognitive function as well aslaboratory measures of synaptic transmission. In the same study, blocking the effects ofmelanotan 1 at the MC4 receptor prevented all of the peptide’s favorable effects[6].
The benefit of melanotan 1 action at the MC4 receptor has been explored in other studiesas well. Investigación, also in mice, shows that MC4 receptor stimulation can boostneurogenesis and lead to cognitive recovery in AD. lt is one of the few studies to showimprovement in the condition rather than simply slowing decline[7]. Once dailyadministration of MT-1 reduces levels of all AD-related biomarkers, indicating that thepeptide actually works through multiple pathophysiological pathways[8].
The MC4 receptor is the only melanocortin receptor known to be expressed onastrocytes, the cells that protect neurons and provide them with nutrition. Research in ratsindicates that melanotan 1 improves astrocyte functioning by increasing levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)[9]. BDNF is critical to protecting synapse stability andneurogenesis in general.
Melanotano 1 and Functional Recovery Following Stroke
It isn’t just biomarkers in AD that improve following MT-1 treatment. Research in gerbilmodels of a stroke lasting ten full minutes reveals that treatment with nanomolar doses otmelanotan 2 can reduce brain damage, including neuron death, and improve recoveringof learning and memory. What is really exciting is that these effects are achieved evenmelanotan 1 is administered 9 hours after a stroke[1oh]. lt is thought that MT-1 activatesrepair mechanisms that improve synaptic plasticity and promote long-lasting functionalrecovery by allowing the brain to reroute learning and memory to healthier areas. Thelynch pin in this process appears to be expression of the Zif268 gene. Zif268 is over-expressed in animals given melanotan-1. The same gene is also over-expressed in themodels of Alzheimer’s disease showing cognitive improvement.
Melanotano 1 influences Heart and Circulation
Research in rats undergoing heart attack has shown that melanotan 1 and othermelanocortins can help to reduce injury and improve circulatory parameters.Administration of MT-1 during CPR and in conjunction with epinephrine helps to restorebaseline arterial pressure and heart rate, reverses metabolic acidosis, reducesinflammatory markers, and improves the expression of genes associated with cardiacfunction. En general, the therapy improved survival rate by 81%, a substantial increase thatmay make melanotan 1 or a similar melanocortin a mainstay of emergency advancedcardiac life support[11].
Melanotano 1 Research and Neuroinflammatory Disease
Research on melanotan 1 has revealed that the MC1 receptor is responsible forpigmentation in skin and hair. For a long time it was thought that this was the receptor’sonly function. Recent research in mice, sin embargo, has indicated that this receptor plays arole in mediating inflammation in the central nervous system. In multiple sclerosis, por ejemplo, helper T cells cause loss of myelin on neurons, which in turn causes neurondysfunction and even death. In mice, administration of melanotan 1 interferes with thisprocess and prevents loss of meylin, thus preventing neuron damage. De hecho,administration of MT-1 to these mice improved myelin recovery and helped to reestablishneuron signaling[12].
Similar effects as above are also seen in mouse models of uveitis, an inflammatorydisorder of the eye that can cause pain and vision loss. Current treatments have a rangeof side effects, so scientists are constantly searching for alternatives to steroids andimmunosuppressive drugs. Alpha-MSH acts to suppress T-cell function, a property mediated through the MC4 receptor and thus mimicked by MT-113. Surprisingly, localadministration of MC4 receptor agonists directly to the eye is as effective as system icadministration. This route of administration helps to eliminate systemic side effects.
Melanotano 1 Investigated in Fat Loss Trials
Melanotano 1 works on several melanocortin receptors, including the MC5 receptor.Stimulation of MC5R promotes the oxidation of fatty acids by muscle and shifts fat cellsfrom fat storage to fat burning[14,, [1s]. These findings in mice also reveal that the fatburning caused by melanocortin stimulation is complex and involves several receptorsand physiologic pathways. dicho eso, melanotan 1 is useful to scientists wishing toexplore how fatty acid metabolism can be altered and offers the tantalizing ability to boostbaseline physiology without the need for exercise, which could be of tremendous benefitin individuals who are unable to exercise due to morbid obesity, disability, or iniury.
Acerca del autor
Investigación por L. Edmiston, MARYLAND. para GURUS DE PEPTIDOS. l. Edmiston tiene un doctorado en medicina. de la Facultad de Medicina de la Universidad Case Western Reserve y una licenciatura. en biología molecular。
References
1.*Effects of a Superpotent Melanotropic Peptide in Combination With Solar UvRadiation on Tanning of the Skin in Human Volunteers Dermatology|JAMADermatology |JAMA Network.”
2.*Effect Of MELANOTAN, [Nle(4),D-Phe(7)]-alpha-MSH, on melanin synthesis inhumans with MC1R variant alleles.-PubMed -NCBl.”[Onlinel. Disponible:https://www,ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16293341.[Accedido: 24-junio-2019].
3.*Afamelanotide and narrowband UV-B phototherapy for the treatment of vitiligo: arandomized multicenter trial.” [Onlinel. Disponible:https://reference.medscape.com/medline/abstract/25230094.[Accedido: 24-Jun20191].
4.*Advances in Vitiligo: An Update on Medical and Surgical Treatments.” [En línea].Disponible:] https://reference,medscape,com/medline/abstract/28210378. [Accedido:24-Jun-20191].
5.“α-MSH analogue attenuates blood pressure elevation in DOCA-salt hypertensivemice.-PubMed -NCBl.”[Onlinel]. Disponible:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23977363.[Accedido: 24-junio-2019]
6.“Melanocortins protect against brain damage and counteract cognitive decline in atransgenic mouse model of moderate Alzheimer’s disease.- PubMed – NCBl.”[En línea]. Disponible: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25034807. [Accedido:24-https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26003413]
7.“NDP-a-MSH induces intense neurogenesis and cognitive recovery in Alzheimertransgenic mice through activation of melanocortin MC4 receptors.- PubMed -NCBl.”[Onlinel.Available]:
8.“Melanocortins protect against progression of Alzheimer’s disease in triple-transgenic mice by targeting multiple pathophysiological pathways. – PubMed -NCBl.”[Onlinel.Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24094579[Accedido:24-Jun-20191.
9.“Melanocortin 4 receptor activates ERK-cFos pathway to increase brain-derivedneurotrophic factor expression in rat astrocytes and hypothalamus. – PubMed -NCB”[Onlinel.Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25892444.[Accedido:24-junio-2019].
10.“Functional recovery after delayed treatment of ischemic stroke with melanocortinsis associated with overexpression of the activity-dependent gene … – PubMedNCBl”[Onlinel.Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19345727[Accedido:24-Jun-20191.
11.“Protective effects of the melanocortin anal0g NDP-a-MSH in rats undergoingcardiac arrest.-PubMed -NCBl.” [En línea]. Disponible:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25446929.[Accedido: 24-junio-2019
12.“Melanocortin-1 receptor activation is neuroprotective in mouse models ofneuroinflammatory disease.-PubMed -NCBl.” [Onlinel. Disponible:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27797962.[Accedido: 24-junio-2019]
13.“Immunosuppressive activity of a novel peptide analog of a-melanocyte stimulatinghormone (a-MSH) in experimental autoimmune uveitis.-PubMed – NCBl.”[OnlineAvailable: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21640392.[Accedido: 24-junio-2019].
14.“Peripheral effect of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone on fatty acid oxidationin skeletal muscle.-PubMed – NCBl.” [En línea]. Disponible:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17127674.[Accedido: 24-junio-2019]
15.“Characterization of murine melanocortin receptors mediating adipocyte lipolysisand examination of signalling pathways involved.- PubMed – NCBl.” [En línea].Disponible: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21616121.[Accedido: 24-junio-2019].